Introduction
Temporomandibular Joint Dysfunction Self-Care Temporomandibular Joint Dysfunction (TMJD), often referred to as TMJ syndrome, is a common condition affecting the jaw joint and muscles that control jaw movement. This disorder can lead to discomfort, pain, and difficulty in chewing and speaking. While professional medical intervention may be necessary in severe cases, many individuals can find relief through effective self-care practices. In this article, we will explore various self-care strategies to manage temporomandibular joint dysfunction and address frequently asked questions.

Understanding Temporomandibular Joint Dysfunction
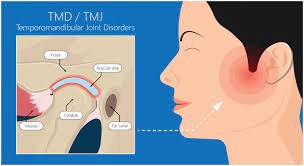
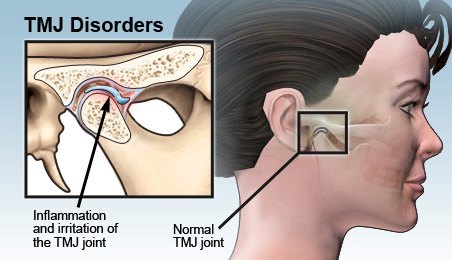
The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) connects the jawbone to the skull and plays a crucial role in activities like talking, chewing, and swallowing. TMJD occurs when there is dysfunction in this joint, resulting in pain and discomfort. Common symptoms include jaw pain, clicking or popping sounds, difficulty in opening or closing the mouth, and headaches.
must read= Saul Abdiel Álvaro
Self-Care Strategies
1. Heat and Cold Therapy
Applying heat or cold packs to the affected area can help alleviate TMJ pain and reduce inflammation. Use a warm compress for 15-20 minutes or an ice pack wrapped in a thin cloth for short intervals. Be cautious not to apply extreme temperatures directly to the skin.
2. Jaw Exercises
Gentle jaw exercises can improve flexibility and strengthen the muscles around the TMJ. Practice simple movements like opening and closing the mouth, side-to-side jaw movements, and stretching exercises. Consult a healthcare professional or a physical therapist for guidance on appropriate exercises.
3. Relaxation Techniques
Stress and tension can contribute to TMJ symptoms. Incorporate relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga into your daily routine. These practices can help reduce muscle tension and promote overall well-being.
4. Avoid Trigger Foods
Certain foods can aggravate TMJ symptoms. Hard, crunchy, or chewy foods, as well as those that require extensive jaw movement, should be limited. Opt for softer alternatives and cut food into smaller, more manageable pieces.
5. Good Posture Habits
Maintaining proper posture, especially for the neck and head, can contribute to TMJ relief. Avoid activities that involve excessive forward head posture, such as prolonged computer use or reading in a slouched position.
6. Over-the-Counter Pain Relief
Non-prescription pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can provide temporary relief from TMJ discomfort. However, it’s essential to follow recommended dosages and consult with a healthcare professional, especially if you have pre-existing conditions or are taking other medications.
7. Night Guards
Bruxism, or teeth grinding, is a common contributor to TMJD. Wearing a night guard can help prevent teeth grinding during sleep, reducing strain on the TMJ. Consult with a dentist to determine if a custom-fitted night guard is necessary.
FAQ
Q1: Can TMJD go away on its own?
A1: In some cases, mild TMJD symptoms may resolve on their own with the implementation of self-care strategies. However, persistent or severe symptoms may require professional intervention.
Q2: When should I seek professional help for TMJD?
A2: If self-care measures do not provide relief or if symptoms worsen, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional. They can assess the severity of the condition and recommend appropriate treatments, such as physical therapy, medications, or, in rare cases, surgery.
Q3: Are there specific foods I should avoid with TMJD?
A3: Yes, individuals with TMJD should avoid hard, chewy, or crunchy foods, as they can exacerbate symptoms. Opt for softer alternatives and cut food into smaller, more manageable pieces.
Q4: Can stress contribute to TMJD?
A4: Yes, stress and tension can contribute to TMJ symptoms. Incorporating relaxation techniques into your routine, such as deep breathing or meditation, may help alleviate stress-related TMJD symptoms.
Q5: Is TMJD more common in certain age groups?
A5: TMJD can affect individuals of any age, but it is more commonly reported among people between the ages of 20 and 40. Factors such as gender, genetics, and trauma may also contribute to the development of TMJD.
Q6: Can I continue to exercise with TMJD?
A6: Gentle exercises that do not exacerbate TMJD symptoms can be beneficial. Consult with a healthcare professional or physical therapist for guidance on appropriate jaw exercises and activities.
Q7: How long does it take for TMJD self-care measures to show results?
A7: The effectiveness of self-care measures varies among individuals. Some may experience relief within a few days, while others may take weeks or months. Consistency in practicing self-care strategies is key to long-term management.
Conclusion
Temporomandibular Joint Dysfunction can be a challenging condition, but effective self-care strategies can significantly contribute to managing its symptoms. It is crucial to be patient and consistent in implementing these measures, and individuals experiencing persistent or worsening symptoms should seek professional guidance. By adopting a holistic approach that combines self-care practices with professional intervention when necessary, individuals with TMJD can enhance their quality of life and minimize the impact of this condition on their daily activities.
